Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions allowing organisms to grow, reproduce, maintain structures, and respond to environments. Metabolism requires enzymes to catalyze transformations within cells.
Metabolism:
Metabolism is a combination of chemical reactions or physical workings of a cell.
Metabolism performs these three functions:
- Assembly of molecules into macromolecules required for a cell; in this process, ATP (an energy carrier) is utilized to form bonds.
- Degrade macromolecules into molecules, this process results in giving off energy (catabolism).
- Conserve energy (in the form of ATP or heat).
Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions:
Chemical reactions either release or require energy. Metabolism is divided into two categories:
Catabolism:
Catabolism is the breakdown of complex organic compounds into simpler ones, while releasing energy.
Anabolism:
Anabolism is the building of complex organic molecules from simpler ones, while absorbing energy.
Metabolism summary

Metabolic Pathways
A metabolic pathway is a sequence of chemical reactions undergone by a compound or class of compounds in a living organism.
Linear metabolic pathway

Divergent metabolic pathway

Convergent metabolic pathway

Cyclic metabolic pathway

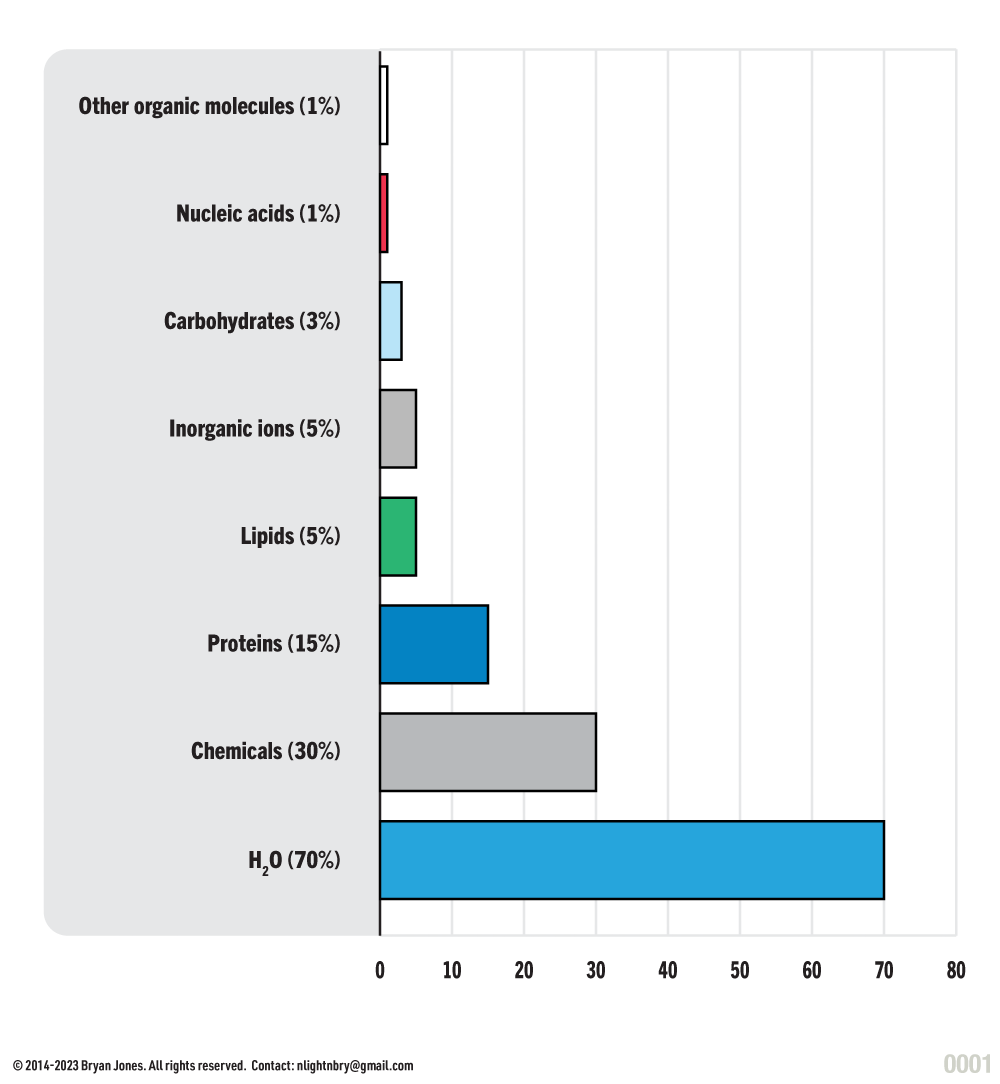
Cellular Composition
There are many types of cells, with different composition. This graphic is to give you an idea of an average cell.
Approximate Composition
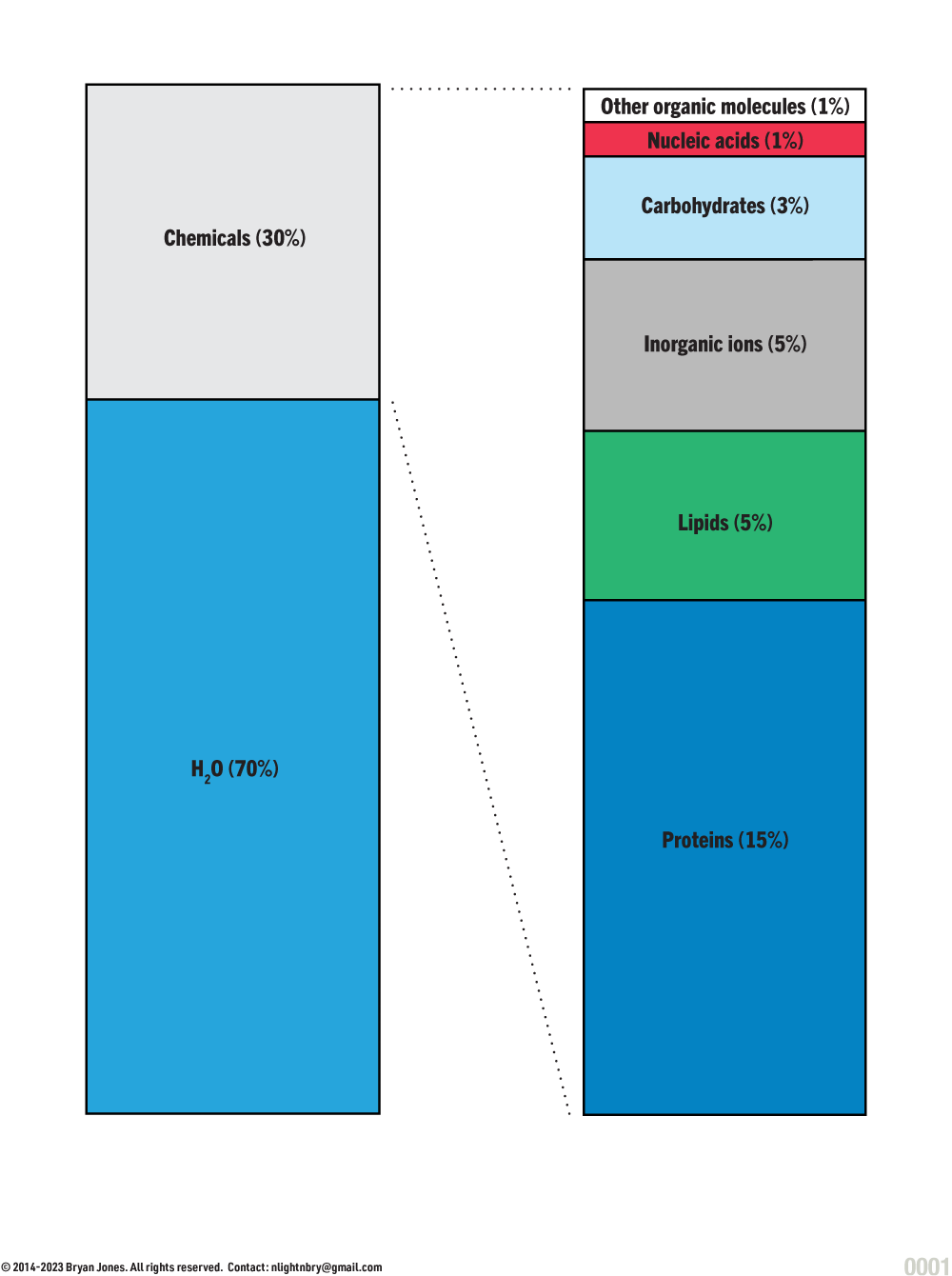
Approximate Composition